Scaling
Autoscaling monitors your Pods and automatically adjusts capacity to maintain steady, predictable performance at the lowest possible cost. With autoscaling, it is easy to set up Pods scaling for resources in minutes. The service provides a simple, powerful user interface that lets you build scaling plans for resources.
This document describes how to scale Pods (Pulsar instances) which are used for running functions, sources, and sinks.
How it works
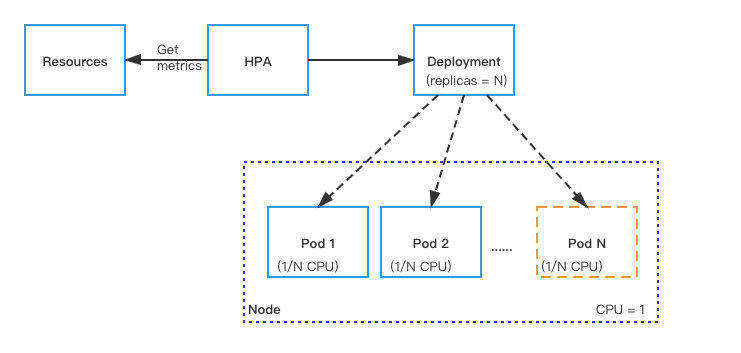
With Kubernetes Horizontal Pod Autoscaler (HPA), Function Mesh supports automatically scaling the number of Pods (Pulsar instances) that are required to run for Pulsar functions, sources, and sinks.
For resources with HPA configured, the HPA controller monitors the resource's Pods to determine if it needs to change the number of Pod replicas. In most cases, where the controller takes the mean of a per-pod metric value, it calculates whether adding or removing replicas would move the current value closer to the target value.
Manual scaling
In CRDs, the replicas parameter is used to specify the number of Pods (Pulsar instances) that are required for running Pulsar functions, sources, or sinks. You can set the number of Pods based on the CPU threshold. When the target CPU threshold is reached, you can scale the Pods manually through either of the two ways:
Use the
kubectl scale --replicascommand. The CLI command does not change thereplicasconfiguration in the CRD. If you use thekunectl apply -fcommand to re-submit the CRD file, the CLI configuration may be overwritten.kubectl scale --replicas="" pod/POD_NAMEUpdate the value of the
replicasparameter in the CRD and re-submit the CRD with thekubectl apply -fcommand.
Autoscaling
Function Mesh supports scaling Pods (Pulsar instances) based on the CPU utilization automatically. By default, autoscaling is disabled (The value of the maxReplicas parameter is set to 0). To enable autoscaling, you can specify the maxReplicas parameter and set a value for it in the CRD. This value should be greater than the value of the replicas parameter.
Auto-scale Pulsar Functions
This example shows how to auto-scale the number of Pods running Pulsar Functions to 8.
Specify the
maxReplicasto8in the Pulsar Functions CRD. ThemaxReplicasrefers to the maximum number of Pods that are required for running the Pulsar Functions.apiVersion: cloud.streamnative.io/v1alpha1
kind: Function
metadata:
name: java-function-sample
namespace: default
spec:
className: org.apache.pulsar.functions.api.examples.ExclamationFunction
forwardSourceMessageProperty: true
maxPendingAsyncRequests: 1000
replicas: 1
maxReplicas: 8
logTopic: persistent://public/default/logging-function-logs
input:
topics:
- persistent://public/default/java-function-input-topic
typeClassName: java.lang.String
output:
topic: persistent://public/default/java-function-output-topic
typeClassName: java.lang.String
# Other function configsApply the configurations.
kubectl apply -f path/to/source-sample.yaml
Auto-scale Pulsar connectors
This example shows how to auto-scale the number of Pods for running a Pulsar source connector to 5.
Specify the
maxReplicasto5in the Pulsar source CRD. ThemaxReplicasrefers to the maximum number of Pods that are required for running the Pulsar source connector.Example
apiVersion: compute.functionmesh.io/v1alpha1
kind: Source
metadata:
name: source-sample
spec:
className: org.apache.pulsar.io.debezium.mongodb.DebeziumMongoDbSource
replicas: 1
maxReplicas: 5
output:
producerConf:
maxPendingMessages: 1000
maxPendingMessagesAcrossPartitions: 50000
useThreadLocalProducers: true
topic: persistent://public/default/destination
typeClassName: org.apache.pulsar.common.schema.KeyValue
resources:
limits:
cpu: "0.2"
memory: 1.1G
requests:
cpu: "0.1"
memory: 1G
# Other configurationsApply the configurations.
kubectl apply -f path/to/source-sample.yaml